A Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) is a formal document outlining standard welding procedures. It serves as a guide for welders and engineers‚ ensuring consistency and quality in welding processes. The WPS is essential for maintaining safety‚ efficiency‚ and compliance with industry standards.
1.1 Overview of WPS
A Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) is a detailed‚ formal document that outlines the specific parameters and guidelines for executing welding operations. It serves as a blueprint for welders‚ ensuring that all welding tasks are performed consistently‚ safely‚ and in compliance with established standards. The WPS typically includes information about the materials being welded‚ the welding method‚ equipment settings‚ filler materials‚ shielding gases‚ and pre- and post-welding treatments. This document is crucial for maintaining the quality and integrity of welded joints‚ particularly in industries where safety and reliability are paramount‚ such as construction‚ aerospace‚ and automotive manufacturing. By standardizing welding practices‚ the WPS helps minimize defects‚ reduces variability‚ and ensures that the final product meets the required specifications and codes. It is often prepared by experienced welding engineers or technicians and must be approved before any welding work begins.
1.2 Importance of WPS in Welding Processes
The Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) plays a critical role in ensuring the quality‚ safety‚ and efficiency of welding operations. By providing a standardized set of instructions‚ the WPS minimizes variability in welding techniques‚ reducing the likelihood of defects and ensuring consistent results. This is particularly important in industries where the structural integrity of welded components is vital‚ such as in aerospace‚ shipbuilding‚ and nuclear energy; The WPS also serves as a legal and technical reference document‚ ensuring compliance with industry codes and standards‚ such as ASME‚ AWS‚ and ISO. Additionally‚ it acts as a training tool for welders‚ guiding them on the proper techniques and parameters to use. Without a WPS‚ achieving certification for welders and validation of welding processes would be challenging‚ leading to potential non-compliance and safety risks. Overall‚ the WPS is a cornerstone of quality control in welding‚ ensuring that all processes are repeatable‚ reliable‚ and meet the required specifications.
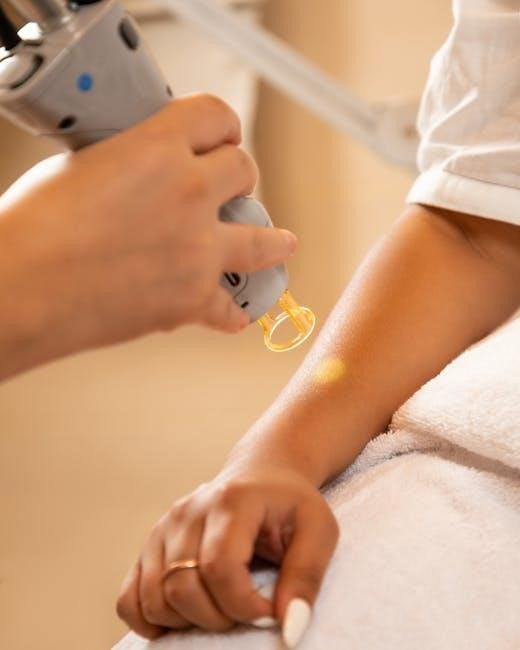
Understanding Welding Procedure Specification (WPS)
A Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) is a detailed written document outlining the parameters‚ methods‚ and materials for specific welding tasks. It ensures consistency‚ quality‚ and safety by adhering to industry codes and standards‚ making it essential across various industries like aerospace and construction.
2.1 Key Components of a WPS Document
A WPS document typically includes detailed information to guide welders and ensure consistent‚ high-quality welds. Key components are the welding process (e.g.‚ MIG‚ TIG‚ SMAW)‚ joint design‚ base metals‚ filler metals‚ and welding parameters like voltage‚ current‚ and travel speed. It also specifies shielding gases‚ preheat and postheat treatments‚ and welding positions. The document may outline quality control measures‚ such as visual inspection or non-destructive testing‚ and reference applicable welding codes or standards. Additionally‚ it includes details about materials‚ equipment‚ and welder qualifications. These components ensure the WPS is comprehensive and aligns with project requirements‚ making it a critical tool for achieving reliable and reproducible welding results.
2.2 Role of the Welder in Adhering to WPS
The welder plays a critical role in adhering to the Welding Procedure Specification (WPS)‚ as they are responsible for executing the welding process accurately. The WPS serves as a detailed guide‚ outlining specific parameters such as arc voltage‚ welding current‚ travel speed‚ and techniques like weave or stringer beads. The welder must strictly follow these guidelines to ensure the integrity and quality of the weld. Deviation from the WPS can lead to non-compliant welds‚ potentially compromising safety and structural integrity. Additionally‚ the welder must use the specified materials‚ such as electrodes and shielding gases‚ and adhere to pre- and post-weld heat treatment requirements. By following the WPS‚ the welder ensures consistency and repeatability in the welding process‚ which are essential for meeting industry standards and codes. Ultimately‚ the welder’s adherence to the WPS is a cornerstone of producing high-quality‚ reliable welds in various industrial applications.

Development of a WPS
Developing a Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) involves a systematic process to ensure weld quality and compliance. It requires understanding the materials‚ welding methods‚ and parameters. The WPS is often prepared by experienced professionals and validated through testing and documentation before final approval.
3.1 Steps to Create a WPS
Creating a Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) involves a systematic approach to ensure compliance with industry standards and project requirements. The process begins with defining the scope of the welding procedure‚ including the materials‚ joint designs‚ and welding processes to be used. Next‚ the relevant welding parameters such as voltage‚ current‚ travel speed‚ and shielding gas must be specified. The WPS must also detail pre-weld and post-weld heat treatment requirements‚ if applicable.
A detailed review of applicable codes and standards is essential to ensure the WPS aligns with regulatory demands. Once the preliminary document is drafted‚ it is typically tested through a Procedure Qualification Record (PQR)‚ which verifies the procedure’s effectiveness. After successful testing‚ the WPS is reviewed and approved by authorized personnel. Finally‚ the document is distributed to the welding team‚ ensuring all parameters are followed during production. This structured approach guarantees the WPS is comprehensive‚ accurate‚ and ready for implementation.
3.2 Preliminary Steps Before Finalizing WPS
Before finalizing a Welding Procedure Specification (WPS)‚ several preliminary steps must be completed to ensure accuracy and compliance. First‚ the materials to be welded‚ including base metals and filler materials‚ must be identified and verified. The joint design and welding method must also be clearly defined. Additionally‚ the welding parameters‚ such as arc voltage‚ current‚ and travel speed‚ need to be established based on the specific application.
Non-destructive testing (NDT) and mechanical testing requirements should be outlined to verify the weld quality. Pre-weld and post-weld heat treatment procedures‚ if required‚ must be detailed. The WPS must also comply with relevant welding codes and standards‚ such as AWS D1.1 or ASME Section IX. Finally‚ a review and approval process involving welding engineers and quality assurance teams ensures the document is complete and meets project specifications before it is implemented.
Qualification and Documentation
Qualification and documentation are critical in ensuring the integrity of welding processes. The Procedure Qualification Record (PQR) serves as the foundational document‚ detailing the parameters used during welding tests. A rigorous qualification process ensures the WPS meets industry standards and project requirements.
4.1 Procedure Qualification Record (PQR)
A Procedure Qualification Record (PQR) is a critical document that records the actual welding parameters and test results used to validate a Welding Procedure Specification (WPS). It serves as proof that the welding procedure meets the specified requirements and industry standards. The PQR is typically generated during the qualification process and includes details such as the materials used‚ welding technique‚ equipment settings‚ and the results of mechanical and non-destructive tests. This document is essential for ensuring that the welds produced under the WPS are consistent and reliable. The PQR is often referenced alongside the WPS to demonstrate compliance with regulatory and quality standards. It is maintained as part of the quality control documentation and is crucial for audit purposes. The PQR is a separate document from the WPS but is closely linked to it‚ as it provides the evidence that the welding procedure is valid and effective. By maintaining a PQR‚ organizations can ensure traceability and accountability in their welding operations.
4.2 Stages of WPS Qualification
The qualification of a Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) typically involves a structured‚ multi-stage process to ensure compliance with industry standards and codes. The first stage is the preparation of a Preliminary WPS‚ which outlines the proposed welding parameters and materials. This document is then used to guide the creation of a Procedure Qualification Record (PQR)‚ which documents the actual welding parameters and test results. The PQR is tested to verify that the weld meets the required mechanical and metallurgical properties. Once the PQR is approved‚ the WPS is finalized and submitted for formal qualification. The final stage involves review and approval by a qualified authority‚ ensuring that the WPS meets all applicable codes and standards. This systematic approach ensures that the WPS is reliable‚ repeatable‚ and compliant with industry requirements. Proper documentation and traceability are maintained throughout the process to ensure accountability and quality control.
Welding Parameters and Variables
Welding parameters and variables are critical elements in a WPS‚ ensuring consistent and high-quality welds. Key parameters include voltage‚ current‚ travel speed‚ and shielding gas flow. Proper control of these variables ensures mechanical properties and defect prevention‚ adhering to industry standards for optimal results.
5.1 Essential Welding Parameters and Their Control
Essential welding parameters are critical variables that directly influence the quality and integrity of a weld. These include welding current‚ arc voltage‚ travel speed‚ welding technique (e.g.‚ weave or stringer bead)‚ and shielding gas composition. Proper control of these parameters ensures consistency and prevents defects. For example‚ welding current affects penetration depth‚ while arc voltage impacts the weld pool size. Travel speed must be optimized to avoid lack of fusion or excessive spatter. Additionally‚ preheating and post-weld heat treatment are critical for managing residual stresses and achieving desired mechanical properties. The WPS document specifies acceptable ranges for these parameters‚ ensuring compliance with industry standards. By adhering to these guidelines‚ welders can produce high-quality joints with minimal variability. Effective control of welding parameters is vital for maintaining safety‚ durability‚ and performance in welded structures. Proper documentation and monitoring of these variables are integral to the success of any welding operation.
Compliance and Standards
Compliance with industry codes and standards is crucial for ensuring the quality and safety of welded structures. The WPS must align with material specifications‚ design requirements‚ and welding codes. Adherence to these standards ensures that welds meet regulatory and performance expectations‚ minimizing risks and guaranteeing reliability.
6.1 Design and Material Specifications
Design and material specifications play a crucial role in the development of a Welding Procedure Specification (WPS). These specifications ensure that the welding process aligns with the mechanical and metallurgical requirements of the materials being joined. The WPS must detail the types of base metals‚ filler metals‚ and any backing materials used‚ as well as their chemical and physical properties. This ensures compatibility and prevents defects or failures in the weld.
The design specifications outline the joint geometry‚ including the groove angle‚ root opening‚ and weld penetration requirements. These parameters are critical for achieving the desired mechanical properties in the finished weld. Material specifications further define the allowable ranges for material thickness‚ strength‚ and ductility‚ ensuring that the weld meets the design intent of the component or structure.
Adherence to industry standards‚ such as ASME or AWS codes‚ is essential for validating the design and material choices. These standards provide guidelines for selecting appropriate materials and welding techniques based on the application and operating conditions of the welded assembly. By clearly defining these specifications‚ the WPS ensures that the welding process is both repeatable and reliable‚ leading to consistent‚ high-quality results.
Documentation of these specifications within the WPS is equally important‚ as it serves as a reference for welders‚ inspectors‚ and engineers. Proper documentation helps prevent deviations from the approved procedures and ensures compliance with quality control measures. Ultimately‚ the integration of design and material specifications into the WPS is fundamental to achieving safe‚ durable‚ and defect-free welds.
6.2 Adherence to Welding Codes and Standards

Adherence to welding codes and standards is a critical aspect of the Welding Procedure Specification (WPS). These codes and standards‚ such as AWS‚ ASME‚ or ISO‚ provide guidelines for ensuring the quality‚ safety‚ and reliability of welds. The WPS must comply with these regulations to guarantee that the welding process meets industry requirements and customer expectations.
Codes and standards dictate specific parameters for welding processes‚ materials‚ and inspection methods. For example‚ they may specify allowable ranges for arc voltage‚ current‚ and travel speed‚ as well as requirements for pre- and post-weld heat treatment. By adhering to these standards‚ the WPS ensures that welds are free from defects and possess the necessary mechanical properties for their intended application.
Non-compliance with welding codes and standards can lead to structural failures‚ safety hazards‚ and costly repairs. Therefore‚ the WPS must be carefully developed and qualified to meet these requirements. Documentation of compliance‚ such as through a Procedure Qualification Record (PQR)‚ further validates the integrity of the welding process. By following established codes and standards‚ the WPS ensures that welds are consistent‚ reliable‚ and meet the highest quality benchmarks.
